Scientists create first of its kind 3d models to fine tune radiation dose
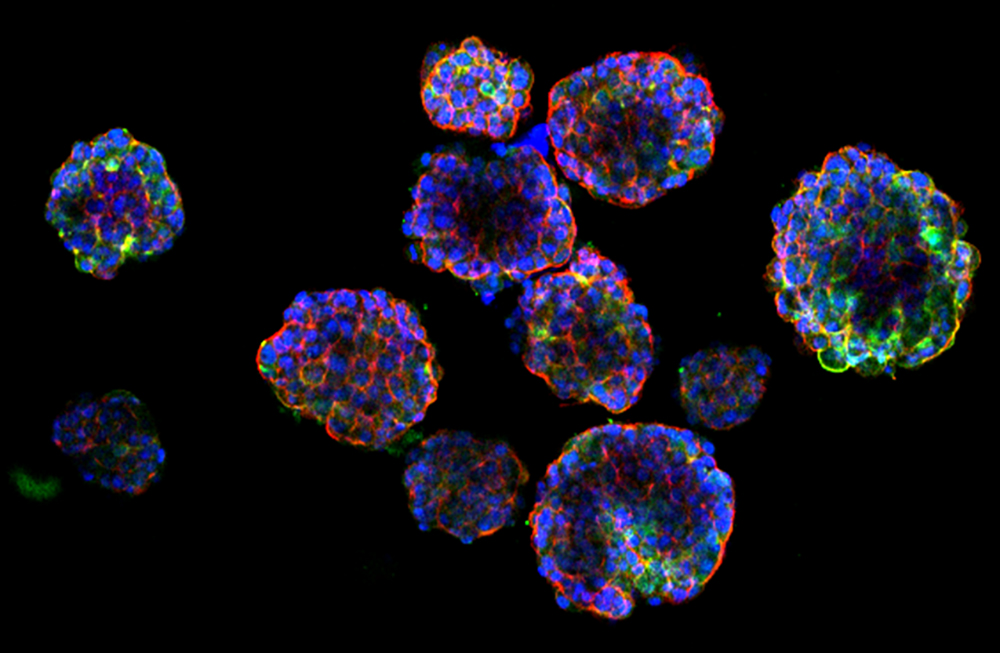
Fluorescence staining of the epithelial markers of the NPC organoids
SINGAPORE, A*STAR’s Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN) has teamed up with Singapore Institute of Advanced Medicine Holdings Pte Ltd (SIAMH) to establish the first of its kind in-vitro patient-derived 3D organoid models of Nasopharyngeal Cancer (NPC).
The study was published in Frontiers in Oncology on 23 February 2021. It is the first direct experimental evidence to predict optimal Radiation Treatment (RT) boost dose required to cause sufficient damage to recurrent hypoxic (low oxygen level) NPC tumour cells, which can be further used to develop dose-painting algorithms in clinical practice.
Two patient-derived xenograft (PDX) lines were used to further establish in-vitro 3D models of hypoxic radioresistant NPC for the first time. This collaboration helps to fine tune radiation treatment, lower the chances of recurrence of NPC and reduce mortality rate.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma is endemic in the east and southeast Asia, where 95% of the cases are invariably associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)1 infection. More than 50% of the patients present with locally advanced and distant metastasis during initial diagnosis, and the 5-year survival rate reduces to between 50% to 70%. The disease is most prevalent in Brunei, Maldives, Indonesia, and Singapore2 .
The current treatment for NPC includes Radiation Treatment. There are recurrent cases which occur due to insufficient radiation. This poses as a clinical challenge to the oncologists. Usually, radiotherapy is used as a re-treatment on inoperable advanced recurrent cases. This results in patients having complications during treatment and the 5-year survival rate will be reduced further. With no relevant in-vitro models to study NPC except the C666-1 cell-line which was established in late 1990’s, the lack of disease-specific in-vitro models of NPC has further hindered development of personalised therapeutic options.
IBN and SIAMH collaborated with the Singapore General Hospital and The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology to create the new in-vitro hypoxic 3D organoid models. These mimicked the hypoxic radioresistant sub-volumes of recurrent NPC, and were found to closely resemble NPC patient tumours.
By using novel patient-derived 3D models, IBN and SIAMH were able to determine experimentally on the radiobiological parameters which provides a better guide in radiation dosing, such that hypoxic radioresistant NPC cells could be eliminated, thus reducing the chances of tumour recurrences.
The study has demonstrated that radiation dose escalation by about 1.4 folds to the hypoxic radioresistant areas in the tumour would further improve the outcome of the treatment. Delivering high dose radiation - in a smaller number of fractions (hypofractionated radiotherapy) may be the way to treat hypoxic radioresistant NPCs. This could reduce long-term side effects, mortality rates due to recurrence, and improve patients’ quality of life.
Dr Lucky Sasidharan, Postdoctoral Fellow at A*STAR’s IBN and first author of the Frontiers in Oncology paper said, “These insights may help to develop personalised radiotherapy regimens and dose painting algorithms which could save time and lives through the prevention of re-irradiation or re-treatment.”
Dr Djeng Shih Kien, Chairman and CEO of SIAMH said, “We are indeed very happy to work with IBN and contribute towards the findings of escalating dose and fractionation of radiotherapy in the treatment of hypoxic radioresistant Nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
The use of in-vitro 3D organoid models of patient-derived xenografts for the first time opens up unlimited opportunities for further research with proton beams when it is available towards the end of 2021 SIAMH’s Proton Therapy Centre is a member of the FlashForwardTM Consortium and it will be extremely exciting to study the effects of Flash Therapy on hypoxic radioresistant 3D models of NPC.”
IBN is planning to work with experts at the Proton Therapy Centre located in Biopolis on this study for evaluating the effects and benefit of utilising Proton therapy and Ultra-High Dose Rate (FLASH) Radiotherapy for the treatment of NPC. These new platforms would also add advantage of delivering very high radiation doses in sub-seconds with high precision targeting on just the areas of the tumours -and sparing the surrounding normal tissues. IBN and SIAMH have been collaborating since 2019 to explore how to better tackle NPC.
Reference:
The paper, ‘Patient-Derived Nasopharyngeal Cancer Organoids for Disease Modeling and Radiation Dose Optimisation’ can be accessed online at https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2021.622244/full (Published in Frontiers In Oncology on 23 Feb 2021)
1 Chen Y-P, Chan ATC, Le Q-T, Blanchard P, Sun Y, Ma J. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet (2019) 394(10192):64–80. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30956-0
2 https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/cancer-trends/nasopharyngeal-cancer-statistics
About the Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN)
The Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (IBN) is the world’s first bioengineering and nanotechnology research institute. Established in 2003, IBN’s mission is to conduct multidisciplinary research across science, engineering and medicine for breakthroughs to improve healthcare and quality of life. IBN’s research activities are focused on Biomedical Devices & Diagnostics and Bioengineering Systems. The Institute has published over 1,200 papers in leading scientific journals, filed over 685 patents and patent applications on its inventions and established 12 spin-off companies. To nurture young research talents, IBN offers students research attachment opportunities and exposure to biomedical research.
About the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR)
The Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) is Singapore's lead public sector R&D agency. Through open innovation, we collaborate with our partners in both the public and private sectors to benefit the economy and society. As a Science and Technology Organisation, A*STAR bridges the gap between academia and industry. Our research creates economic growth and jobs for Singapore, and enhances lives by improving societal outcomes in healthcare, urban living, and sustainability. A*STAR plays a key role in nurturing scientific talent and leaders for the wider research community and industry. A*STAR’s R&D activities span biomedical sciences to physical sciences and engineering, with research entities primarily located in Biopolis and Fusionopolis.
About Singapore Institute of Advanced Medicine Holdings Pte Ltd
Proton Therapy Pte Ltd, a subsidiary of the Singapore Institute of Advanced Medicine Holdings Pte Ltd (SIAMH), will provide proton beam therapy treatment in Singapore. It is part of a new oncology center that is located at Biopolis, Singapore. The new comprehensive oncology center includes a diagnostic center providing both imaging and laboratory services using advance medical technologies, nuclear medicine, theranostics, radiotherapy and also health screening. Its training facility, the Advanced Medicine Training Centre, will provide the necessary training to the specialists in this part of the world. For more information, search proton.sg.
A*STAR celebrates International Women's Day

From groundbreaking discoveries to cutting-edge research, our researchers are empowering the next generation of female science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) leaders.
Get inspired by our #WomeninSTEM
