FACES OF A*STAR
A*STAR Launches EV Battery Testing And Disassembly Line, As Part Of Wider Efforts To Build Battery Remanufacturing Capabilities
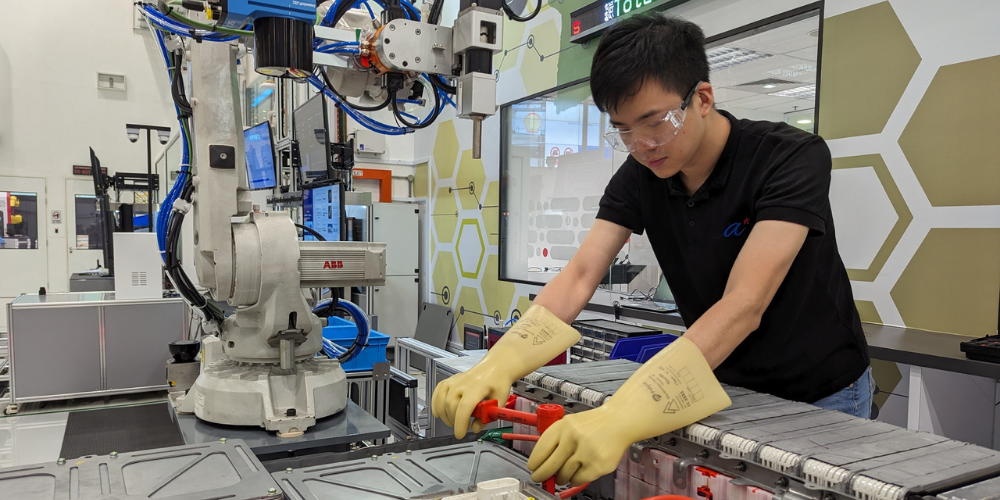
Pack Inspection and Disassembly station of the EV Battery Testing and Disassembly Line at A*STAR Advanced Remanufacturing and Technology Centre (A*STAR ARTC)
SINGAPORE – During the Industrial Transformation Asia-Pacific (ITAP) 2023 event, the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) announced a new Electric Vehicle (EV) Battery Testing and Disassembly Line. This is part of wider efforts by A*STAR’s research institutes such as the A*STAR Advanced Remanufacturing and Technology Centre (A*STAR ARTC), A*STAR Singapore Institute of Manufacturing Technology (A*STAR SIMTech), A*STAR Institute of Materials Research and Engineering (A*STAR IMRE), A*STAR National Metrology Centre (A*STAR NMC), and A*STAR Institute of High Performance Computing (A*STAR IHPC), to work with partners in building a circular economy for batteries through the development of key remanufacturing processes and systems solutions.
The line, located within A*STAR ARTC, leverages Industry 4.0 technologies including automation, robotics, intelligent vision inspections, and diagnostics, to improve current practices of disassembling EV battery packs which can be dangerous, tedious, and labour-intensive. The line will also be used to assess the performance and physical conditions of batteries, such as wear and tear.
With the electrification of transportation, retired EV batteries are expected to pile up, increasing the need for effective solutions to manage them sustainably. Improper disposal of batteries can pose threats to human health and environment, and there is also a growing demand for the raw materials used in battery manufacturing. Recycling allows the recovery of materials for the manufacturing of new batteries. Retired batteries may also retain some useful life that can be repurposed for less demanding applications before they are recycled.
Both repurposing and recycling pathways require the disassembly of EV battery packs, and manual disassembly is a labour-intensive process as these packs come in diverse shapes and sizes, as well as physical and performance conditions. It can take more than seven hours to manually disassemble a battery pack, which consists of numerous modules that need to be disassembled further into individual cells. A battery pack is also typically held together by multiple fasteners of varying types, often numbering in the hundreds, that need to be removed during disassembly. Additionally, human operators are required to come into physical contact with EV battery packs, including their high voltage cables and wiring which operate at voltages ranging from 400 to 800 volts. Even when discharged, these packs can still hold residual power that pose risks to a human, in some cases, up to 10 per cent of their charge capacity.
Automating parts of the disassembly process, such as visual inspection and the unbolting of fasteners, can reduce human exposure to high-voltage situations and speed up the process by an estimated 50 per cent.
The line will also feature technologies for faster and more accurate measurements of batteries’ State-of-Health (SOH), which is an indicator of the batteries’ remaining useful life and how this compares to original capacity or performance capabilities. Current industry-accepted SOH measurements require the EV battery pack to undergo a complete charge and discharge cycle at a slow fixed rate, taking up to seven hours typically. Under the current line, A*STAR ARTC is now able to quickly determine the SOH in 30 minutes at the battery cell level. It will look to scale this up to the battery module level, to simultaneously evaluate the condition of both individual cells and module and to better understand a module’s overall health.
A*STAR ARTC worked with knowledge partner McKinsey & Company on practical applications of Industry 4.0 technologies on the line, aiming to improve industry safety standards for handling high voltage battery packs, increase productivity in high mix and low volume scenarios, and standardise the handling of EV batteries. This includes using augmented reality (AR) to guide employees in a step-by-step fashion for testing and disassembly processes, an energy management system to optimise energy usage of the line, and a modular set-up supported by automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to increase flexibility of the line in adapting to changes in testing and disassembly needs. For example, a user of the line can easily increase its capacity in battery pack inspection by increasing the number of stations that can check the physical conditions of these packs.
“A*STAR’s launch of the EV Battery Testing and Disassembly Line marks a significant milestone in our commitment to building a circular economy for batteries. This will set the foundation for important research and translational work in the remanufacturing and recycling of batteries. The new platform will use Industry 4.0 technologies for safe and efficient management of EV batteries, and we are excited to work with like-minded partners like McKinsey & Company on this development journey. We hope this novel approach will spur the industry to develop more applications for managing retired EV batteries,” said Dr David Low, CEO, A*STAR ARTC, A*STAR.
Kaushik Das, Managing Partner, Southeast Asia, McKinsey & Company said, “As electric vehicle (EV) adoption surges in the region, we need to be innovative in scaling digital solutions to better manage end-of-life (EOL) EV batteries. Together with A*STAR A*STAR ARTC via McKinsey’s Innovation and Learning Center, we introduced the EV Battery Testing and Disassembly Line, through which we are able to determine different methods to enhance battery circularity. Furthermore, the EV Battery Testing and Disassembly Line is also able to tackle critical issues in process efficiency, safety, and standards compliance. This ongoing partnership enables us to continue being changemakers in new technology development and capability building, which in return will contribute to the local and regional economy.”
To further develop technologies for commercial deployment, A*STAR will partner battery recyclers that are looking to disassemble significant volumes of EV battery packs at the end of their useful lives, and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) that plan to develop new technology offerings for the growing end-of-life battery market.
ANNEX A – SET-UP OF THE EV BATTERY TESTING AND DISASSEMBLY LINE
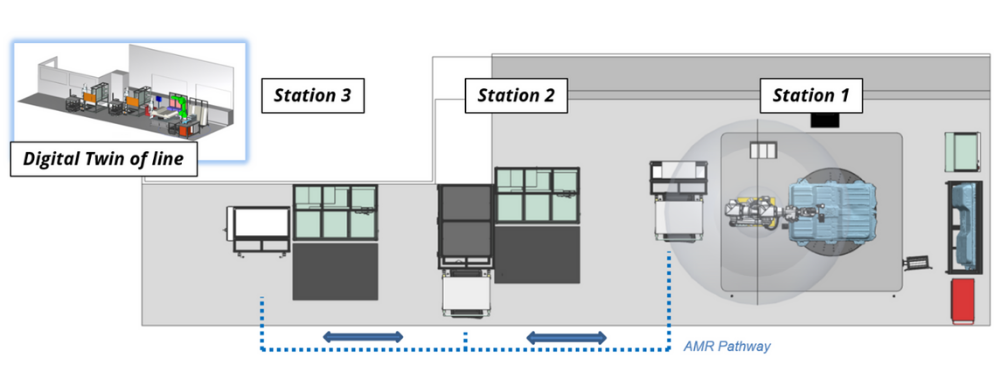 Diagram of the EV Battery Testing and Disassembly Line
Diagram of the EV Battery Testing and Disassembly Line
The EV Battery Testing and Disassembly Line features three different stations, and a digital twin which shows a virtual representation of the platform to enable real-time monitoring.
Station 1: Pack Inspection and Disassembly
To disassemble EV battery packs
- Checking battery packs’ physical condition, for example, wear and tear
- Automated unbolting on battery packs
- Removing and disconnecting wiring within battery packs assisted by AR
- Removal of busbars and metal brackets assisted by AR
- Automated transfer of battery module to station 2 via AGV
Station 2: Module Discharging and Disassembly
To discharge module and disassemble module to cell- Assessing battery modules’ physical condition for safe disassembly
- Discharging battery module before disassembling
- Monitoring energy usage and potential energy recovered from discharging
- Disassembling of module to cells, after safety testing and discharging
- Automated transfer of battery cells from station 2 to station 3 via AGV
Station 3: Rapid Cell Grading
To determine State of Health (SOH) measurements and next steps- Rapid assessment of State of Health (SOH) of battery cell
- Smart tracking of waste generated from disassembly of battery packs
- Monitoring overall carbon emissions across the line, and gathering data to guide process towards achieving net zero
- Monitoring overall carbon emissions across the line, and gathering data to guide process towards achieving net zero
Digital Twin of Line
To enable digitalisation of the line and its operations at various stages- Validating and improving layout and processes through physics-based modelling, and re-optimising line capacity
- Digitalising operations for real-time visibility, such as energy consumption and overall equipment effectiveness
- Planning and scheduling jobs for timely completion
About the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR)
The Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) is Singapore's lead public sector R&D agency. Through open innovation, we collaborate with our partners in both the public and private sectors to benefit the economy and society. As a Science and Technology Organisation, A*STAR bridges the gap between academia and industry. Our research creates economic growth and jobs for Singapore, and enhances lives by improving societal outcomes in healthcare, urban living, and sustainability. A*STAR plays a key role in nurturing scientific talent and leaders for the wider research community and industry. A*STAR’s R&D activities span biomedical sciences to physical sciences and engineering, with research entities primarily located in Biopolis and Fusionopolis.
Was this article helpful?
A*STAR celebrates International Women's Day

From groundbreaking discoveries to cutting-edge research, our researchers are empowering the next generation of female science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) leaders.
Get inspired by our #WomeninSTEM




