The Silent Epidemic: Chronic Wound Impact
Chronic wound is a silent epidemic that affects approximately 2% of the world’s population1 and has negative economical and societal impacts. The burden of chronic wounds treatment grows rapidly due to high wound healing costs (US$3.9K per wound)2, an aging population (estimated to reach 1.6 billion by the year 2050) and rise in the incidence of diabetes (estimated to reach 552 million by 2030) worldwide.
The trend of increasing chronic wounds is introducing a significant burden to the healthcare staff, particularly the nurses who will need to manage and treat the chronic wounds since current clinical practice for chronic wound management is manual, subjective, and time-consuming.
Chronic wounds present significant challenges for patients and healthcare providers, requiring precise monitoring and timely interventions. However, the current manual methods of wound assessment can be time-consuming and subjective, leading to potential inaccuracies and delays in treatment.

Enhancing Patient Care Through Efficient Wound Analysis
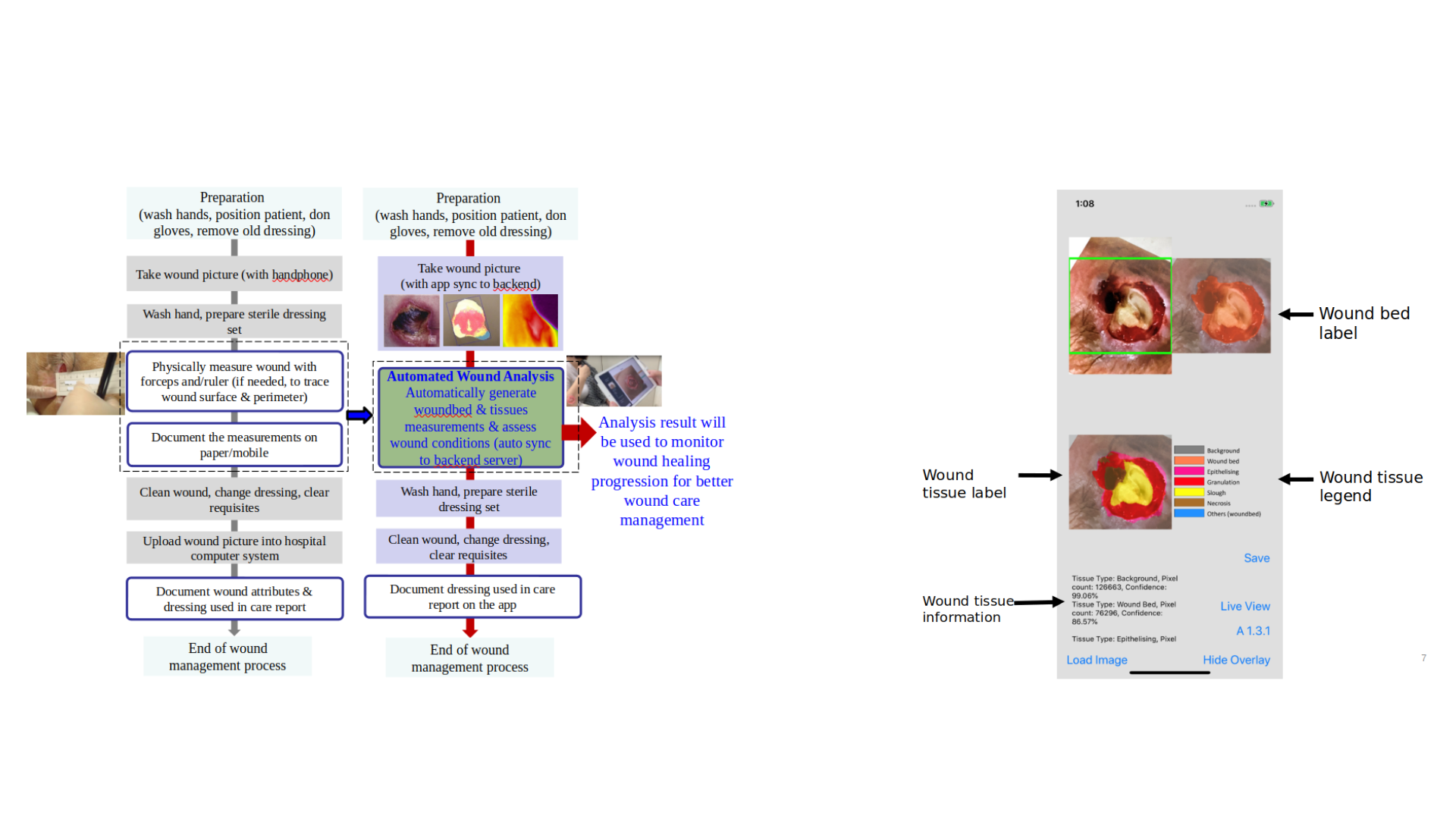
Currently, the nurses perform manual measurements using a ruler to visually estimate the size of the wound bed and the tissues’ sizes/compositions, as accurate physical manual measurements are too tedious. Experience is required to correctly gauge the various wound tissue type for specific wound treatment type to be applied.
Therefore, we developed an Automated WOund Management Analysis system (AWOMA) that can assist healthcare nurses with automated analysis of wounds, including automated segmentation and measurements of the size of the wound bed and the automatic classification of wound tissues and their sizes.
Automating Wound Analysis
The AWOMA system consists of an automatic and efficient deep learning-based customised image segmentation architecture that is designed to have high accuracy, while having lower complexity (with a much smaller number of parameters and model file size) than typical deep-learning-based image segmentation network. Thus, it can be effectively incorporated into mobile Apps of mobile devices without needing internet access and without requiring a backend server to perform the processing and diagnosis.
The AI model's compact size enables rapid loading onto mobile devices, facilitating quick execution of wound bed segmentation and tissue classification tasks. Upon capturing a color image of the wound with the device's built-in camera, the AI swiftly performs these tasks in mere seconds.
In the figure below, the process on the left demonstrates the current process in clinics (estimated to take about 36 minutes), and the process on the right shows AWOMA process which reduces the time spent by 40% (estimated to take about 20 minutes).
Future Plans for AWOMA: Predictive Wound Healing
The AWOMA system will be enhanced with the introduction of new functions such as wound healing prediction. This function will aid wound care professionals in forecasting non-healing wounds within the next 3 to 6 months. By alerting doctors and nurses, they can administer proactive treatments to facilitate more effective healing process of chronic wounds in their patients.
Recognition and Awards for AWOMA
Some accolades of this AWOMA system are listed below:
- Best Poster Merit Award in the International Conference on Biomedical Engineering (ICBME) in Dec 2019. (earlier version of AWOMA)
- One of the licensee’s medical device received CE Mark (Nov 2020) & HSA Medical Device certification (Jul 2021), and was featured in main-stream media: Channel News Asia (2021), Channel 8 (2019), Wan Bao (2018), Shin Min (2018).
- Awarded the Grand Prize Winner of 2021 Healthy Aging Prize for Asian Innovation (HAPI) and Winner of 8th Asia Pacific Eldercare Innovation Awards 2020.
1. Krister Järbrink, et al., “Prevalence and incidence of chronic wounds and related complications: a protocol for a systematic review”, Systematic Review, 2016 Sep 8;5(1):152.
2. Caroline Fife, Marissa Carter, “Wound Care Outcomes and Associated Cost Among Patients Treated in US Outpatient Wound Centers_ Data From the US Wound Registry”, Wounds, 2012; 24(1),10–17.
Contact us for further collaboration discussions and potential opportunities







