I²R Research Highlights
Finding any Waldo with zero-shot invariant and efficient visual search
New insight into Human Visual search mechanism's efficiency and effectiveness
Visual search of a target object in a cluttered scene is a fundamental challenge in our daily visual tasks and most computer vision approaches do not leverage insight from mechanism that guides such human visual search.
Our biologically inspired computational model, Invariant Visual Search Network (IVSN) was developed to closely mimic human visual search capability in four key properties of visual search.
- Selectivity (locate target in a cluttered scene)
- Invariance (locate target despite change in its appearance)
- Efficiency (locate target fast without exhaustive sampling)
- Zero-Shot Training (find novel targets despite minimal or zero prior exposure to them)
Previous work on visual search has focused on searching for exact matches of a target after extensive category-specific training.
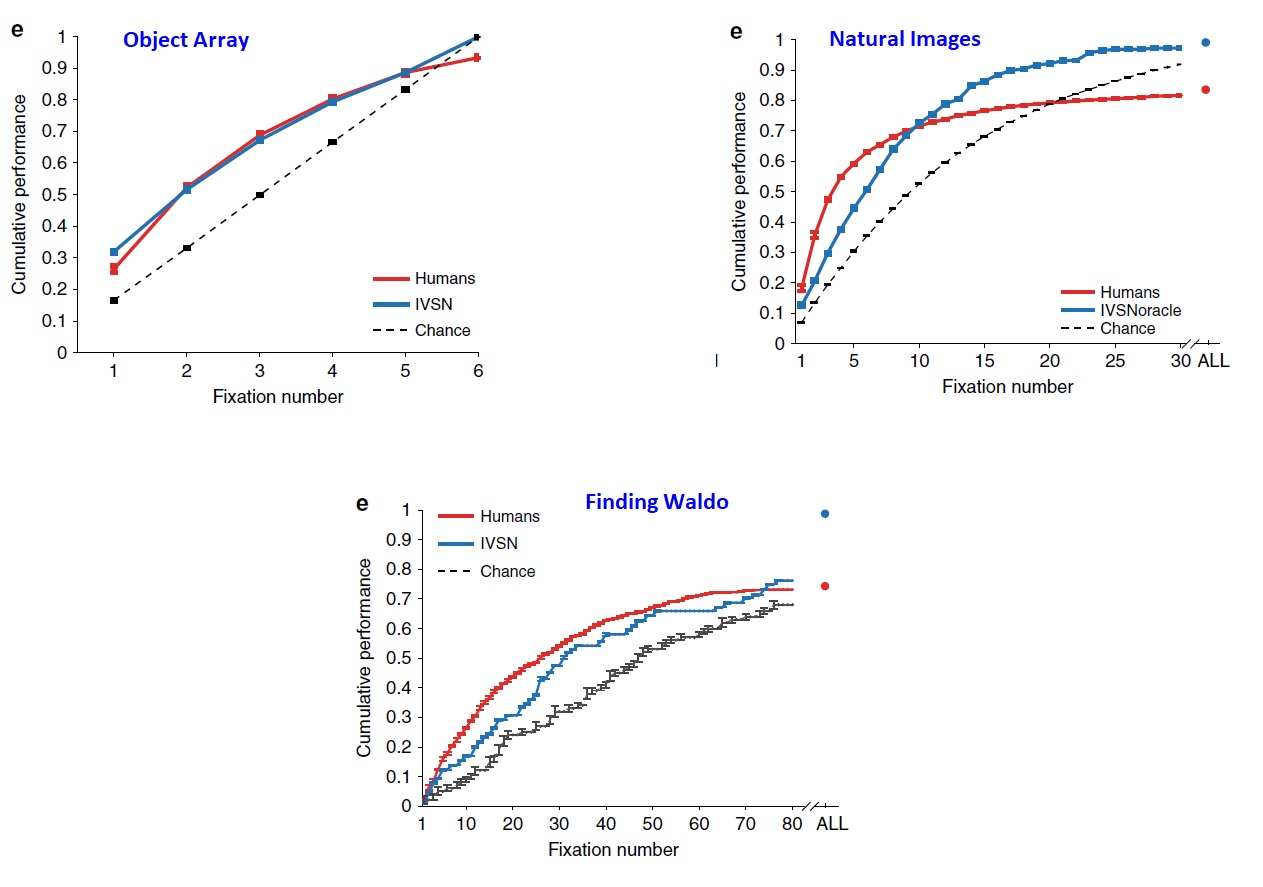
In the visual search experiments, 3 scenarios were tested using 45 subjects.
- Searching for a target within an array of Objects (Object Array)
- Searching for a target in natural scenes (Natural Images)
- Searching for Waldo (Finding Waldo)
This model can be applied to medical imagery for anomaly detection, robot navigation and search in crowded area, and suspicious/ abnormal item detection in security checks etc.
The A*STAR-affiliated researchers contributing to this research are from the Visual Intelligence department of Institute for Infocomm Research as well as contributions from National University of Singapore, Harvard Medical School and University of Minnesota Twin Cities.
Featured in:
A*STAR celebrates International Women's Day

From groundbreaking discoveries to cutting-edge research, our researchers are empowering the next generation of female science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) leaders.
Get inspired by our #WomeninSTEM
