IHPC Tech Hub
IHPC Tech Hub showcases IHPC's suite of in-house developed applications, tools or technology to help you unlock the possibilities to overcome business challenges. Through providing valuable insights, you can now predict and shape the commercial outcomes, automate processes, and free up resources for repetitive and labour-intensive tasks.
Discover the power of computational modelling, simulation and AI that brings about positive impact to your business.
Discover the power of computational modelling, simulation and AI that brings about positive impact to your business.
- Health & Human Potential
- Manufacturing & Engineering
- Smart Nation & Digital Economy
- Transport & Connectivity
- Urban Solutions & Sustainability
Human-Robot Collaborative Artificial Intelligence (Collab AI)
25 Jan 2023
The Human-Robot Collaborative Artificial Intelligence (Collab AI)# programme aims to enable robots to perform as team members alongside humans by understanding tasks, procedures and human actions, as well as learning quickly and robustly.
The goal is to have robots work together with humans in complex and dynamic tasks that cannot be easily automated, but where robots can still assist humans in doing parts of the task that may be ergonomically difficult or dangerous for humans, or
require skills that robots are good at, such as performing repetitive actions with high precision.
Moreover, because of limitations in robot sensing and intelligence, specialised set-ups are currently required for robots to be deployed with humans. Collab AI seeks instead to develop technologies that enable robots to adapt to humans and work
safely in human environments, for example:
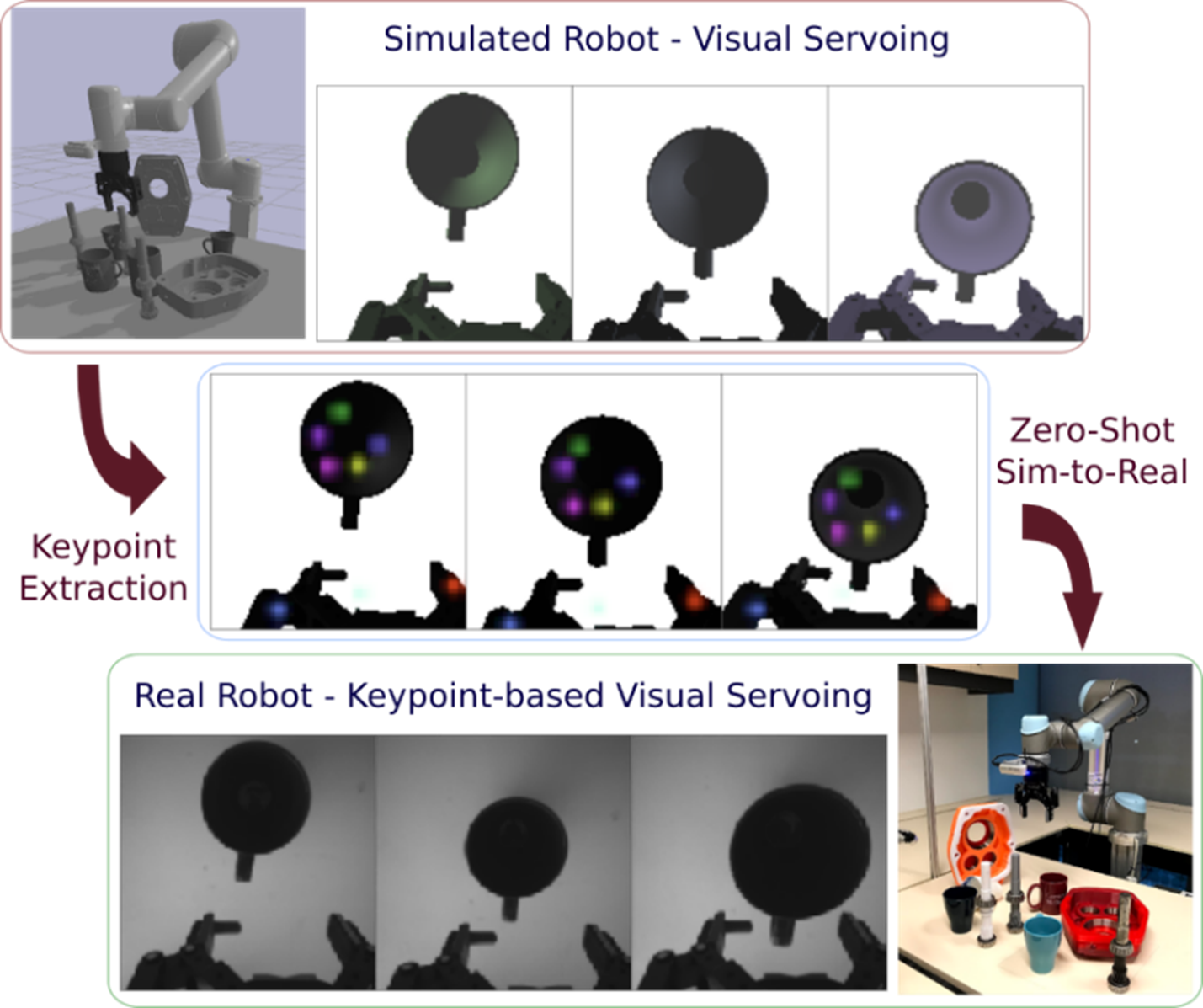
- Learning to recognise new objects through visual self-exploration
- Learning new tasks by observing human demonstration and teaching, which allows non-experts to work with robots without needing to explicitly program them
- Collaborating naturally with humans on tasks with visual & tactile guidance, natural speech/dialogue interaction and AR interface
In this way, Collab AI technologies help to reduce cost and increase the flexibility of robot deployments, making them suitable for high-mix, low-volume (HMLV) use cases, such as hyper-personalised manufacturing.
Features
Features
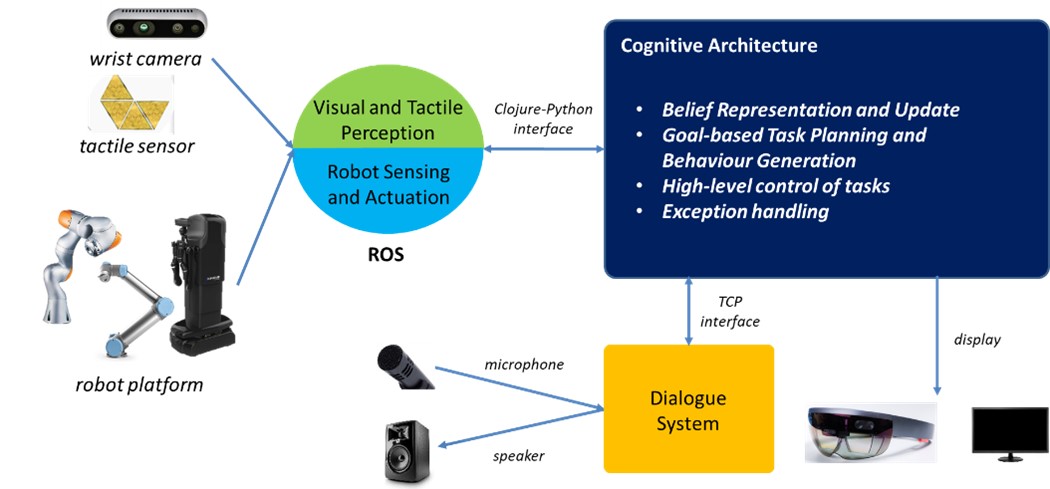
The Collab AI programme is developing a human-robot collaborative system solution that:
- Enables natural collaboration with humans
- Integrates multi-modal perception and dialogue capability
- Leverages commonsense knowledge
- Uses a cognitive architecture as a basis for integration
- Stays agnostic to the robotic platform
- Supports learning from instructions and/or demonstrations
The Science Behind
Industry Applications
Collab AI technologies can be applied to complex tasks that cannot be fully automated and require human inputs to allow robots to be deployed more effectively to augment humans. Other possible applications include work-cells for hyper-customised manufacturing with easy process adaptation through robot teaching.
Currently, Collab AI technologies are being trialed in:
- Collaborative automated programming for testing consumer products
- Collaborative harvesting of edible plants
#Collab AI is an AME Programmatic Programme led by IHPC in collaboration with I2R, ARTC, NUS, NTU and SUTD.
A*STAR celebrates International Women's Day

From groundbreaking discoveries to cutting-edge research, our researchers are empowering the next generation of female science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) leaders.
Get inspired by our #WomeninSTEM
.png?sfvrsn=ff199933_15)
.png?sfvrsn=6b8397fa_1)