Collaborative Industry Development
SIMTech assists industry through consortia and collaborative industry development projects (CIPs) to bring together companies with similar needs and provide opportunities for cost-sharing and work within the industry ecosystem. Some examples are showcased here.

CIP for Carbon Footprint Quantification via Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
The SIMTech Collaborative Industry Project (CIP) for Carbon Footprint Quantification via Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is an innovative and collaborative initiative led by the Singapore Institute of Manufacturing Technology (SIMTech). It aims to advance sustainability practices in various industries, ensuring continuity beyond a singular LCA project and reporting.

CIP on E-TraM OTP (Electric Traction Module Open Technology Platform)
Over the past few years, there has been a rapid transition of internal combustion engine powertrains to electrified powertrains around the world. A*STAR SIMTech is pleased to introduce the E-TraM OTP CIP Programme (Electric Traction Module Open Technology Platform Collaborative Industry Project) to our industry partners. This will be a neutral platform that serves as a catalyst to speed up the local electrification activities of powertrains, which cover e-machines, inverters, and powerful battery systems.

CIP on Process Development of Cabin Seat Modules and Components
SIMTech has helped SIAEC and four SMEs to upgrade their knowledge in the design, simulation, and manufacturing of polymeric materials and transferred the technologies to them. As a result of this CIP, the four SMEs have developed their capabilities and have since been approved as SIAEC’s service providers which created the primary avenue for the SMEs to venture into the high value-add aviation industry business. This effort also captures value for Singapore, as local SMEs can be qualified suppliers.

CIP on Dental Crown Innovation
Seven dental labs joined this CIP to evaluate the feasibility of implementing low-cost 3D stereo lithography to manufacture dental crowns and bridges. They have evaluated the feasibility of applying 3D printing to replace the typical manual skills and craftsmanship of the local dental lab. The project also demonstrated the production of zirconia crowns using SIMTech-developed resin to replace expensive CAD/CAM and milling processes. Some dental labs are in the process of adopting the 3D printing process.
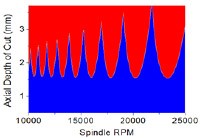
CIP on Advance Machining Techniques
This CIP aims to improve the productivity and surface quality of precision machining via Quick Milling Vibration Solver (DynaCut) which helps to eliminate machining chatter and improve the surface finishing of machined parts caused by vibration. Eight companies have adopted the technology and have experienced improvement in machining productivity of 30–50% through time, labour cost reduction, and improvements in the surface quality of the machined part.

CIP on Item Management and Tracking System (IMTS)
This CIP was launched in 2013 and the IMTS was developed to track assets and take stock. To date, 20 CIPs have been initiated, and 106 companies have benefited from this technology. In 2015, 48 companies had deployed the technology, and companies have reported productivity improvements of 20% to 90% for asset management and inventory stock-taking. One example is Ichiban Sushi which has adopted and implemented the Supply Chain Track & Trace technology in five of their 24 outlets with plans to roll out the technology to other outlets.

CIP on Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
This CIP was launched to maximise machine effectiveness by conducting an OEE assessment to pinpoint key losses and root causes and then find ways to improve productivity through procedure changes and advanced monitoring and control technologies. Key personnel were trained on the shop floor OEE model and the five key steps of the OEE methodology. 20 companies involving 95 personnel that participated in this programme have reported productivity improvements: tooling down time reduction of 30–60%, machine idle time reduction of 30-70%, rework and defect reduction of 15–40%, machine breakdown reduction of15–40% and throughput improvement of 10–15%.
A*STAR celebrates International Women's Day

From groundbreaking discoveries to cutting-edge research, our researchers are empowering the next generation of female science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) leaders.
Get inspired by our #WomeninSTEM
.png?sfvrsn=843a4005_8)