Boosting intranasal mRNA delivery with muco-penetrating lipid nanoparticles
Science
Intranasal vaccination offers a promising strategy for inducing sterilizing immunity in the upper respiratory tract, the primary entry point for airborne viruses like SARS-CoV-2 into the body. However, effective nasal delivery of mRNA remains a significant challenge due to the mucus network, which creates a physical barrier that traps foreign materials and facilitates their removal. To overcome this barrier, we have engineered muco-penetrating lipid nanoparticles having a liquid core and a near-neutral surface in the mucosal pH range, which renders them with high deformability to enable easier movement in the mucus without being trapped by highly negatively charged mucin. When nasally dosed to mice, these nanoparticles induced greater mRNA translation and antigen-specific mucosal IgA response than the benchmark Comirnaty formulation, highlighting their potential for effective intranasal mRNA vaccination1.
Societal Impact
Currently available COVID-19 mRNA vaccines are given by intramuscular injection and activate robust systemic immunity but weak mucosal immunity, which therefore provides ineffective protection against respiratory infection of SARS‐CoV‐2. Our muco-penetrating, liquid-core lipid nanoparticles demonstrated their capability to cross the nasal mucosa and facilitate the delivery of mRNA vaccines beyond the underlying epithelium, ultimately stimulating the production of mucosal IgA antibodies in mice. If successfully implemented, such nasal mRNA vaccines could contribute to strengthen our preparedness against future outbreaks by effectively blocking human-to-human spread of pathogenic viruses via a respiratory route.
Technical Summary
Intranasal vaccination has several advantages over conventional intramuscular vaccination, such as ease of administration, high patient compliance, and the potential ability to activate both mucosal and systemic immunity. However, mRNA vaccines are confronted with many challenges at mucosal surfaces, such as poor mucus penetration and rapid mucociliary clearance. In this study, we reported muco-penetrating, liquid-core lipid nanoparticles capable of delivering mRNA vaccines across nasal mucosa. Following nasal administration in mice, these nanoparticles achieved approximately 60-fold greater mRNA translation in the nasal cavity and elicited stronger SARS-CoV-2 spike-specific mucosal IgA responses compared to Comirnaty formulation, without causing any severe inflammation. These findings provide promising insights into the design of nasally deliverable mRNA formulations for diverse prophylactic applications.
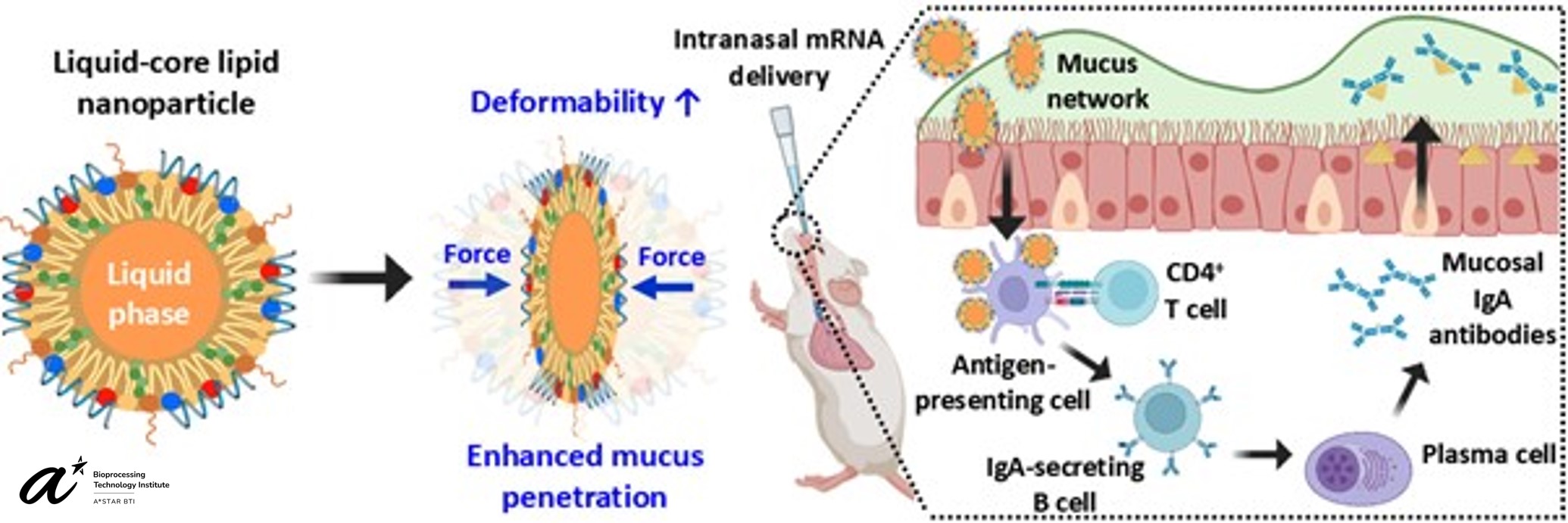
Figure 1. Design of muco-penetrating lipid nanoparticle having a liquid core and a near-neutral surface for enhanced intranasal delivery of mRNA vaccines
References
1. N. Maniyamgama §, K. H. Bae §, Z. W. Chang, J. Lee, M. J. Y. Ang, Y. J. Tan, L. F. P. Ng, L. Renia, K. P. White, Y. Y. Yang, Muco-Penetrating Lipid Nanoparticles Having a Liquid Core for Enhanced Intranasal mRNA Delivery, Advanced Science 12 (2025) 2407383 (§ denotes equal contribution) https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202407383
A*STAR celebrates International Women's Day

From groundbreaking discoveries to cutting-edge research, our researchers are empowering the next generation of female science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) leaders.
Get inspired by our #WomeninSTEM
.png?sfvrsn=1a7df424_3)