Profiling meat species using a novel glycomic workflow
Science
Proteins have sugars called glycans that play an essential part in the regulation of physiological and pathological functions of organisms. It is therefore important to characterise and control the consistency of these glycans in biomedical studies and drug development. In this research study, we have delved into the characterization of glycans in the meat product. Our novel glycomic workflow uses a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based approach to identify the distinct glycan profiles of chicken, pork and beef. As an added bonus, this high-resolution workflow is capable of identifying specific sugars α-galactose and sialic acid (Neu5Ac) which are implicated in human diseases like allergies and cancer. Our process could contribute by providing another validation approach for meat species differentiation and food safety monitoring.
Societal Impact
Food fraud is the deceitful labelling of meat species, geographical origin, and quality. This non-compliance costs the global food industry around USD$ 6.2 to USD $40 billion annually. To overcome this, novel and robust quantitative methods are needed to profile meat samples. In this study, we have demonstrated the use of glycomic workflow as an orthogonal approach in meat species profiling and that it could be exploited in the future for the authentication of meat origin and quality.
Technical Summary
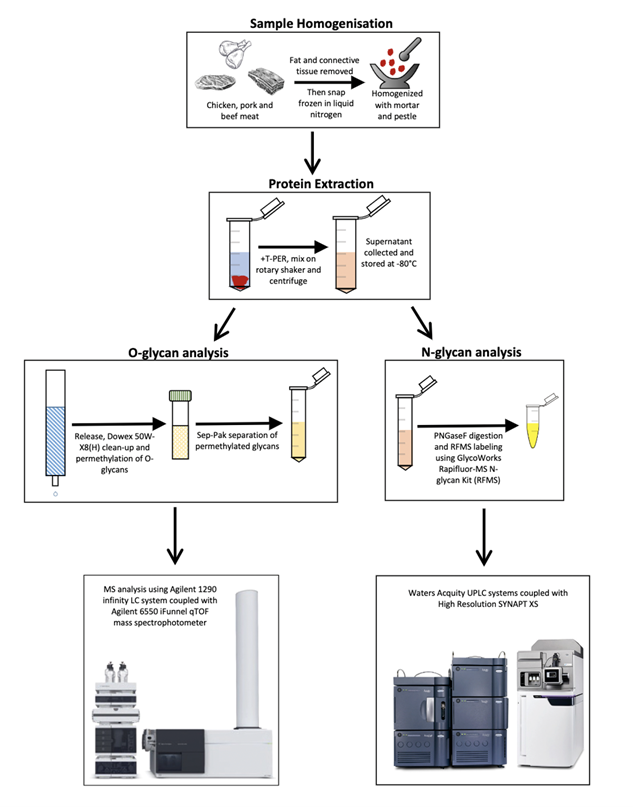
The glycomic workflow involves an experimental approach in extracting and isolating glycans from chicken, pork, and beef samples. It is then followed by quantitative glycomic analysis of O-glycan and N-glycan abundances, and the computation of the principal component analysis (PCA) to differentiate meat sample species based on the glycan structures and their abundances.
References
Chia, S., Teo, G., Tay, S.J., Loo, L.S.W., Wan, C., Sim, L.C., Yu, H., Walsh, I. and Pang, K.T., 2022. An Integrative Glycomic Approach for Quantitative Meat Species Profiling. Foods, 11(13), p.1952.
A*STAR celebrates International Women's Day

From groundbreaking discoveries to cutting-edge research, our researchers are empowering the next generation of female science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) leaders.
Get inspired by our #WomeninSTEM
.png?sfvrsn=1a7df424_3)