Advanced Spatial Omics with Quantum and Generative AI

LAU MAI CHAN
 | LAU Mai Chan Senior Scientist Email: Lau_Mai_Chan@a-star.edu.sg Research Group: Advanced Spatial Omics with Quantum and Generative AI |
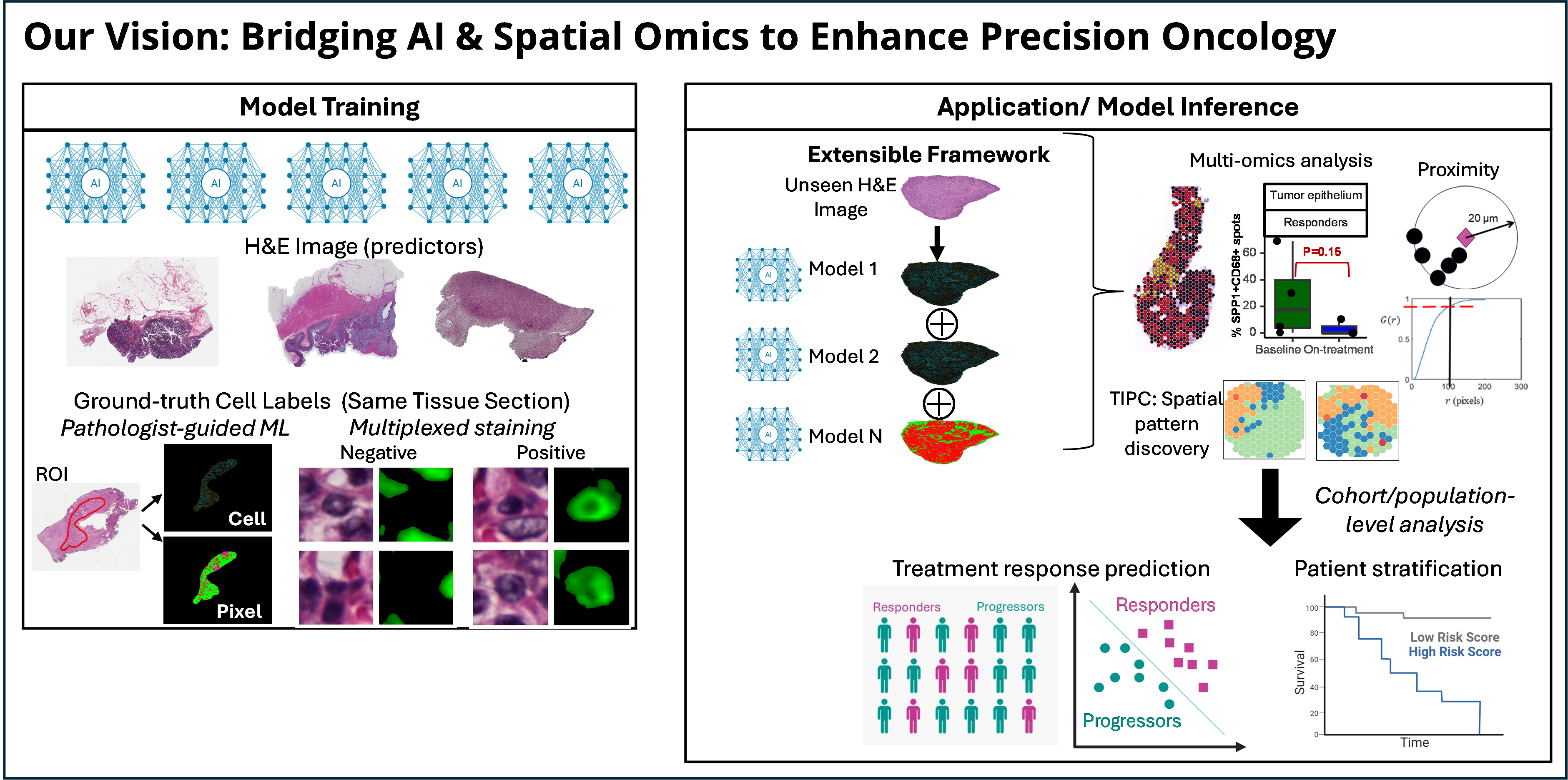
Mai Chan Lau earned her PhD from the National University of Singapore, focusing on high-performance GPU research. She began her postdoctoral training at the Singapore Immunology Network, focusing on single-cell immunology bioinformatics. She then moved to Boston, USA, where she leveraged Al for Molecular Pathological Epidemiology studies, using tissue-based multi-marker technology at Harvard Medical School’s teaching hospitals. In 2021, she returned to Singapore and joined the Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, expanding her research to spatial transcriptomics and Al. In 2022, she established her own laboratory at the Bioinformatics Institute, concentrating on advanced spatial multi-omics studies using Al and quantum computing. Concurrently, she leads the Computational Immunology Platform at the Singapore Immunology Network.
GROUP MEMBERS
| Research officer | TAN Wei Kit |
| Research Officer | CHEONG Jiasheng Isaac |
| Research Officer | ZHANG Qiao Yan Marcia |
A*STAR celebrates International Women's Day

From groundbreaking discoveries to cutting-edge research, our researchers are empowering the next generation of female science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) leaders.
Get inspired by our #WomeninSTEM